Illumination
Types of white lighting
"White" is not the same as "White"
Even 'white' light can be produced in a variety of ways. Depending on the problem, lighting requirements, object size and installation dimensions, the following are
-
LED illumination
-
Halogen incandescent lamps
-
Fluorescent light (high frequency)
LED lighting plays a special role in image processing. Their characteristic properties, such as long life, mechanical robustness and the ability to be placed in almost any shape of housing, make them ideal for use. Their light colour can be not only white, but also red, green, blue, infrared or even ultraviolet. This makes it possible to solve applications that would not be possible with other types of lighting. The majority of industrial image processing applications are therefore based on LED lighting, with halogen lamps still being used almost exclusively in the field of hyperspectral imaging. Fluorescent tubes are used for large-area hall lighting, but also in colour measurement as standard light tubes (e.g. D65).

The concept of colour temperature
Not every white light source appears to have the same shade of white to the viewer. With colour (and monochrome) camera systems, it is also possible to see colour effects in the images or significant shifts in grey values.
The following four images were taken with the colour camera (no IR cut filter in front of the sensor glass) on default settings with no additional white balance to show the clear differences in the light spectrum. (Some of the effects could be compensated for with a white balance function, some could not).

Daylight
Image has normal colours as seen by the human eye. White reference area on left is light grey

White LED
Blue logos (top left) brightened, image has a cooler overall colour effect due to blue cast

White fluorescent lamp
White reference surface appears yellow-green, green tones are slightly lighter

Halogen lamp/ camera without IR cut
White reference surface appears orange-red, image completely discoloured due to many yellow and red tones and low contrast.
Where does this term come from?
Colour temperature is measured and reported in Kelvin (K) and is a measure of the colour appearance of a light source. The spectrum visible to the human eye is between 2,790 and 11,000 Kelvin.
The physical explanation for this is Max Planck's definition of a 'black body'. A black body absorbs all incident radiation and reflects none. The colour temperature is the temperature of the black body at which its light emission produces the same colour impression as the actual illumination.
A black body at 5500K has a radiation spectrum that is close to that of daylight.
Each type of lighting has an individual light spectrum with a different distribution over the visible wavelength range and different intensities. An incandescent lamp has a continuous spectrum, but with the typical bell-shaped intensity distribution of a black-body lamp. Metal halide lamps, fluorescent lamps and LEDs even emit in very specific wavelength ranges.
Colour temperature of different illumination types
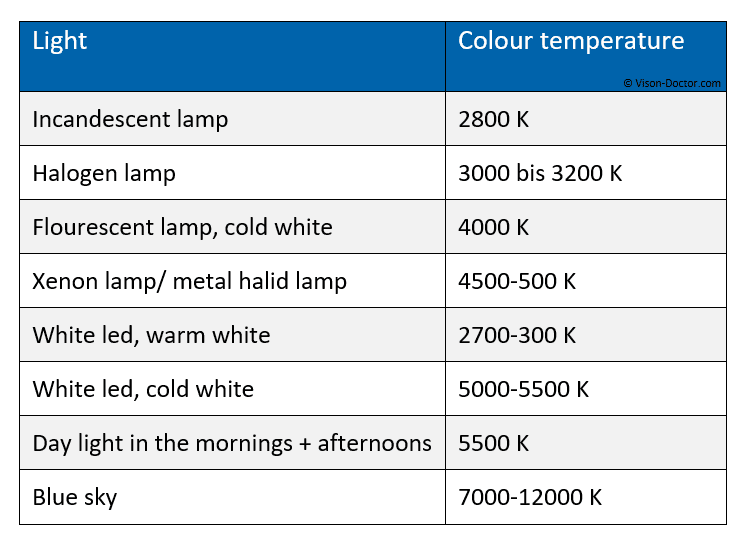
Important for Machine Vision
-
Depending on the ‘white’ lighting used, a more or less coloured camera image results. White LED lighting appears very bluish, images from fluorescent lamps appear greenish. Halogen lamps produce a very yellowish colour impression in the camera image due to the increased red and infrared component.
-
Exposure to extraneous light and daylight greatly change the character of the coloured light and should be avoided in colour applications. Shield the test area! The sensitivity of the camera sensor is also not the same for different colours. Additional distortion effects occur.
-
The sensitivity of the camera sensor is also not the same for different colours. Additional distortion effects occur. These inhomogeneous RGB colour components can be corrected by a white balance. This is partly done in the camera, on the frame grabber or with the help of software on the PC.
-
During the ageing process, the colour temperature of the lighting shifts. Halogen lamps glow darker, i.e. have more red components, while the fluorescent dyes in white LEDs are destroyed and the native blue emission becomes more prominent. Regular calibration is required here.
-
When using white light, optical errors can occur in the resulting video image with both colour cameras and monochrome cameras. The longitudinal and transverse chromatic aberration can be compensated for using high-quality optics to avoid these colour or grey fringes.
-
A simple solution to avoid this effect with monochrome cameras is to use monochromatic light (blue, green, red etc.), such as that produced by LEDs. The result is higher-contrast images.
Need machine vision lighting ?
Vision-Doctor.com is a private, independent, non-commercial homepage project and not a technology provider or system integrator. Suitable technologies and further professional support can be obtained from the companies & partners listed below.
If necessary, I will be happy to provide a quick recommendation, contacts and brief information.















