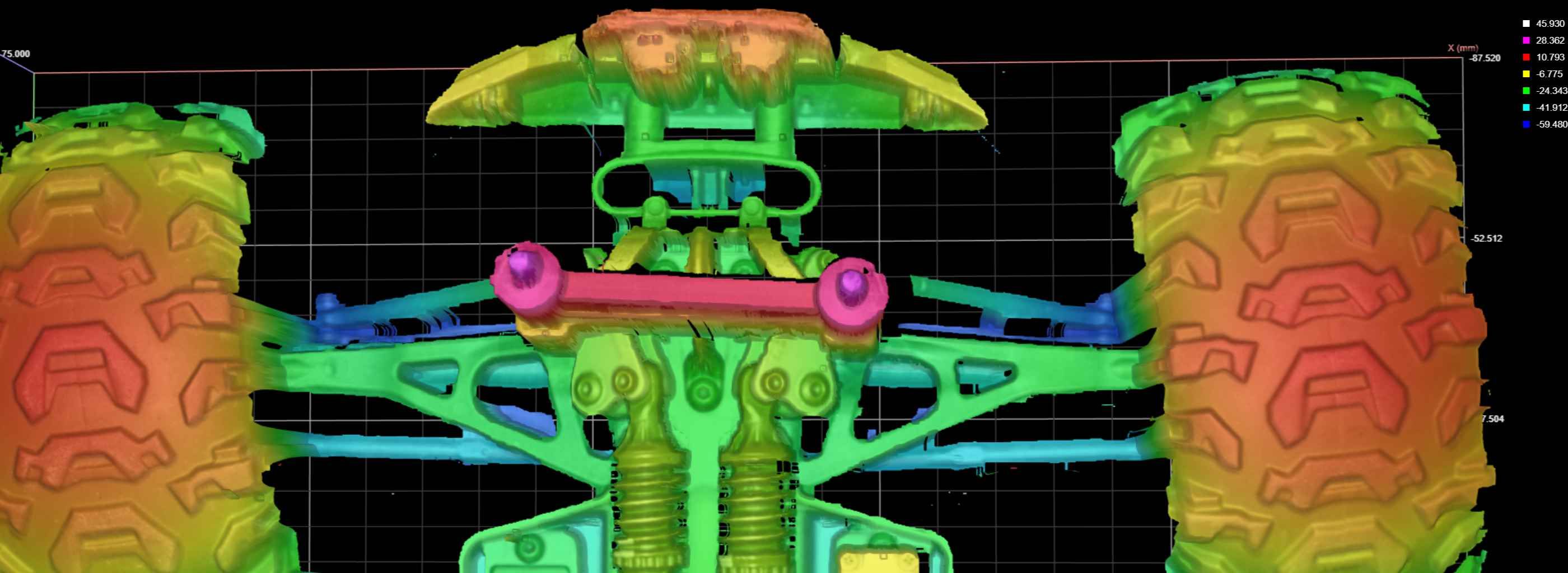
Systems
Laser Triangulation
Laser triangulation is used in a wide range of applications. It is used for quality control, surface inspection and to create detailed 3D scans. Its high accuracy and versatility make it a valuable technology in modern machine vision industry.
A laser line is projected onto the target and the deformation of this line is analysed by the geometry of the target. Laser triangulation enables the precise measurement of heights, contours and volumes down to single digit microns.
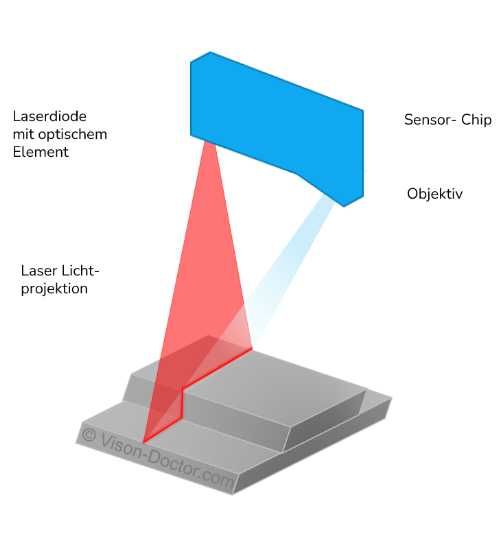
Working principle of laser triangulation
Laser line projection onto the object
In laser triangulation, a laser line is projected onto the object to be measured. This projection is usually made from above to ensure a clear line of sight between the laser and the object.
Acquisition of the laser profile
A camera captures the full image including the profile generated by the laser line on the surface sensor. This single image shows how the laser line is distorted by the surface of the object, allowing conclusions to be drawn about the shape of the object.
Creation of a complete 3D point cloud
To generate a complete 3D point cloud, many such laser profiles must be captured. This requires often hundred or thousands of images, which are taken in stages and combined with each other.
Movement of the object or sensor
To capture the required profiles, either the object or the sensor must be moved. This makes it possible to capture different perspectives of the surface and create a complete 3D image.
Use of an encoder to avoid distortions
An encoder is used to avoid distortions in the transport direction. This ensures that the movement is measured precisely and that the captured profiles can be merged correctly.
Scanning with laser triangulation
True, accurate measurement in space is possible because the true 3D shape of the part is known.

Benefits of laser triangulation
1. Independent of the grey tones of the object
Laser triangulation focuses on the height information of the object and is therefore independent of the grey tones of the object. This allows consistent measurement regardless of the brightness of the material.
2. High x resolution
High x resolution is possible with laser triangulation. Typically, up to 4K resolution can be achieved with a single sensor, allowing precise detail to be captured.
3. high z accuracy
Thanks to the sub-pixel laser line detection process, laser triangulation can achieve Z accuracy in the micrometre range. This is particularly important for smaller regions of interest (ROIs).
4. Dense 3D point clouds
The method provides 3D data for each individual sensor pixel, resulting in dense and detailed 3D point clouds. These point clouds provide a comprehensive representation of the object surface.
5. grey tone inspection
In addition to height information, intensity images can also be catured. This allows additional classic 2D inspection of other features of the object.
6. Robustness to ambient light
Sharp-banded bandpass filters ensure that only laser light is transmitted, increasing measurement accuracy. At the same time, intense monochromatic lasers are used.
Potential disadvantages
1. Motion of sensor or object needed
To acquire the required laser profiles, either the sensor or the target must be moved. This movement requirement can add to the complexity of the application.
2. The need for an encoder
An encoder is required to accurately capture the movement and avoid distortion. This results in additional hardware requirements.
3. Additional cost for handling & encoder
The integration of handling systems and encoders can add costs that must be considered when implementing laser triangulation.
4. Potential occlusion effects
The triangulation angle can cause shadowing. This can be compensated for by using two sensor heads, but this can increase complexity and cost.
5. Monochromatic laser
The use of a monochromatic laser can be problematic if the object is coloured and the laser colour is absorbed by the complementary object colour. This can significantly affect the exposure time.
Need help selecting a system?
Vision-Doctor.com is a private, independent, non-commercial homepage project and not a technology provider or system integrator. Suitable technologies and further professional support can be obtained from the companies & partners listed below.
If necessary, I will be happy to provide a quick recommendation, contacts and brief information.















