



















CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors are an essential component of almost all industrial cameras. These sensors are characterised by their ability to convert light into electrical signals. Each individual pixel cell contains an amplifier circuit that reads the signal directly. This enables faster and more flexible image processing than with CCD sensors, and makes CMOS sensors superior in many areas.
One of the biggest advantages of CMOS sensors is the high frame rate, and in addition to the ability to record full images, modern sensors can read out the sensor in various ways. For example, pixels can be binned before image transmission or only one or more sections can be defined to be read out. In this way, the data rate can be reduced or the frame rate can be massively increased.
Binning in industrial cameras is a technique that combines neighbouring pixels of an image sensor. This is done either by adding brightness values on the sensor itself or by software processing on the FPGA. Pixels can be binned horizontally, vertically or in both directions.
However, binning always reduces the resolution of the image by reducing the number of effective pixels. It is therefore important to find the right balance between sensitivity and resolution, depending on the application.
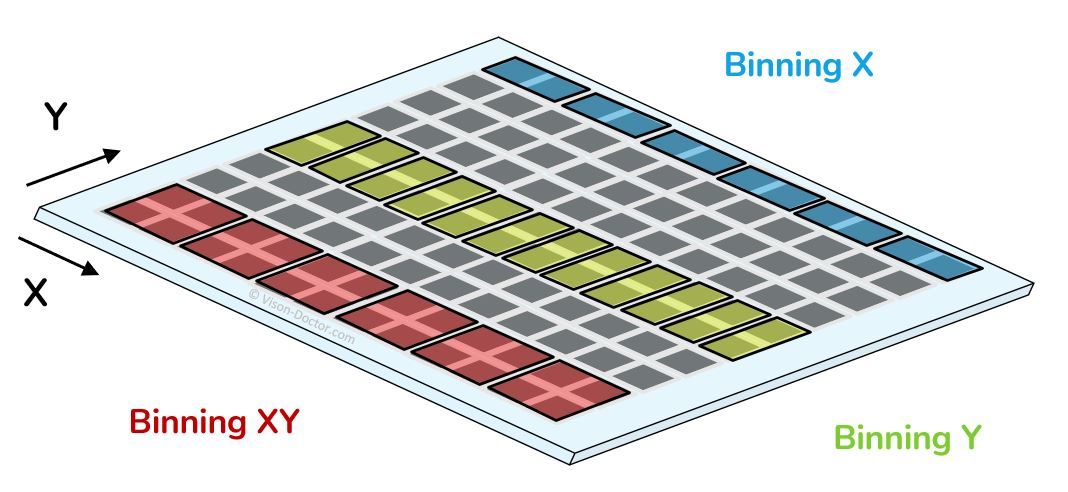
Analog binning:
The brightness values of neighbouring pixels on the sensor are added together. This increases the camera's frame rate because fewer pixels need to be read.
Digital binning:
The brightness values are added together after digital conversion. This can be done in software or by a digital signal processor after the analogue-to-digital converter. The image brightness is also higher, but the frame rate of the sensor during image capture is not increased.
Advantages of binning
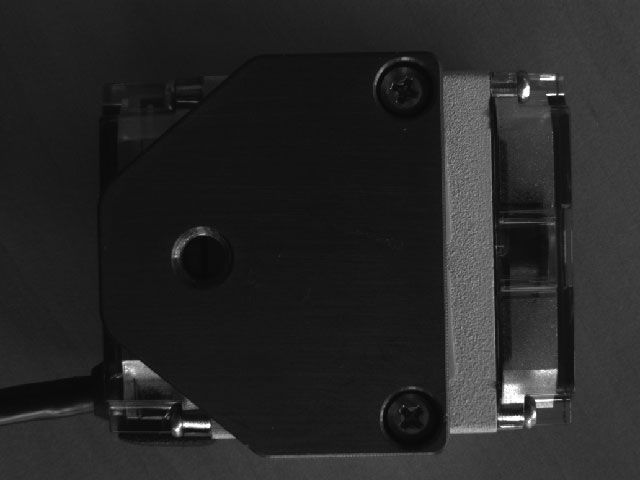
Full resolution without binning. However, the image is too dark in places for the software processing.
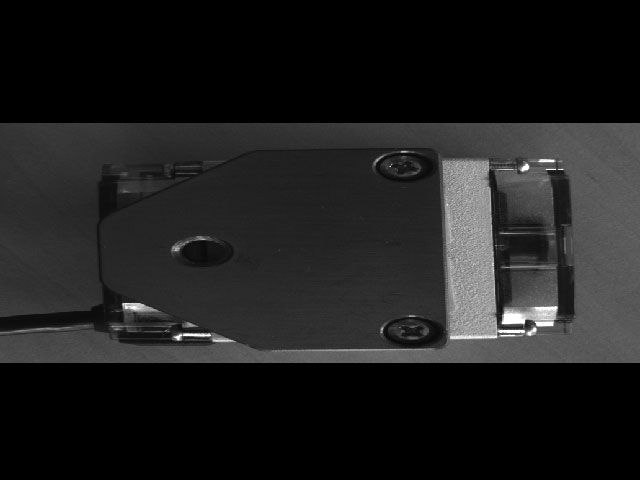
Camera sensitivity doubled, but image only has half the resolution in the Y direction.
Resolution halved in each direction, a new pixel is calculated from four pixels. Four times the sensitivity of the sensor.
The partial scan function of industrial cameras allows only a specific region of interest (ROI) to be captured and processed.
With modern CMOS cameras, the ROI can be selected almost at will. In most cases, however, it makes sense to select the image section centred on the optical axis due to the optics.
By taking a smaller field of view, the camera can capture more frames per second without exceeding the maximum data rate of the device. Depending on the readout method, the frame rate increases approximately in proportion to the reduction in the total area. Exact formulae for the maximum frame rate when using ROIs can usually be found in the camera manual.
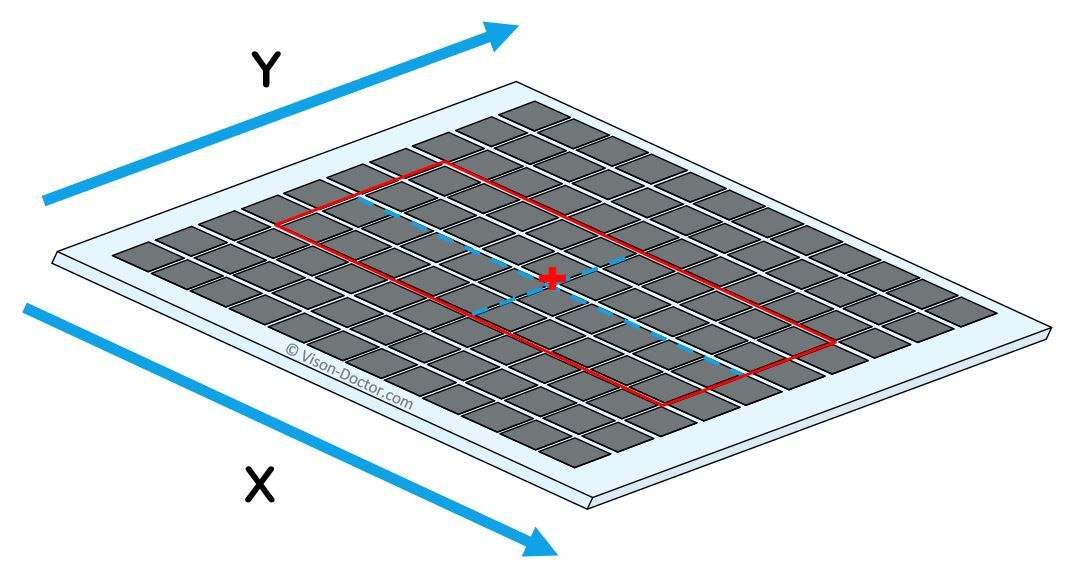

Camera sensor is completely read out.

In partial scan mode, only a region of the sensor is read out and transmitted. The frame rate of the camera increases.
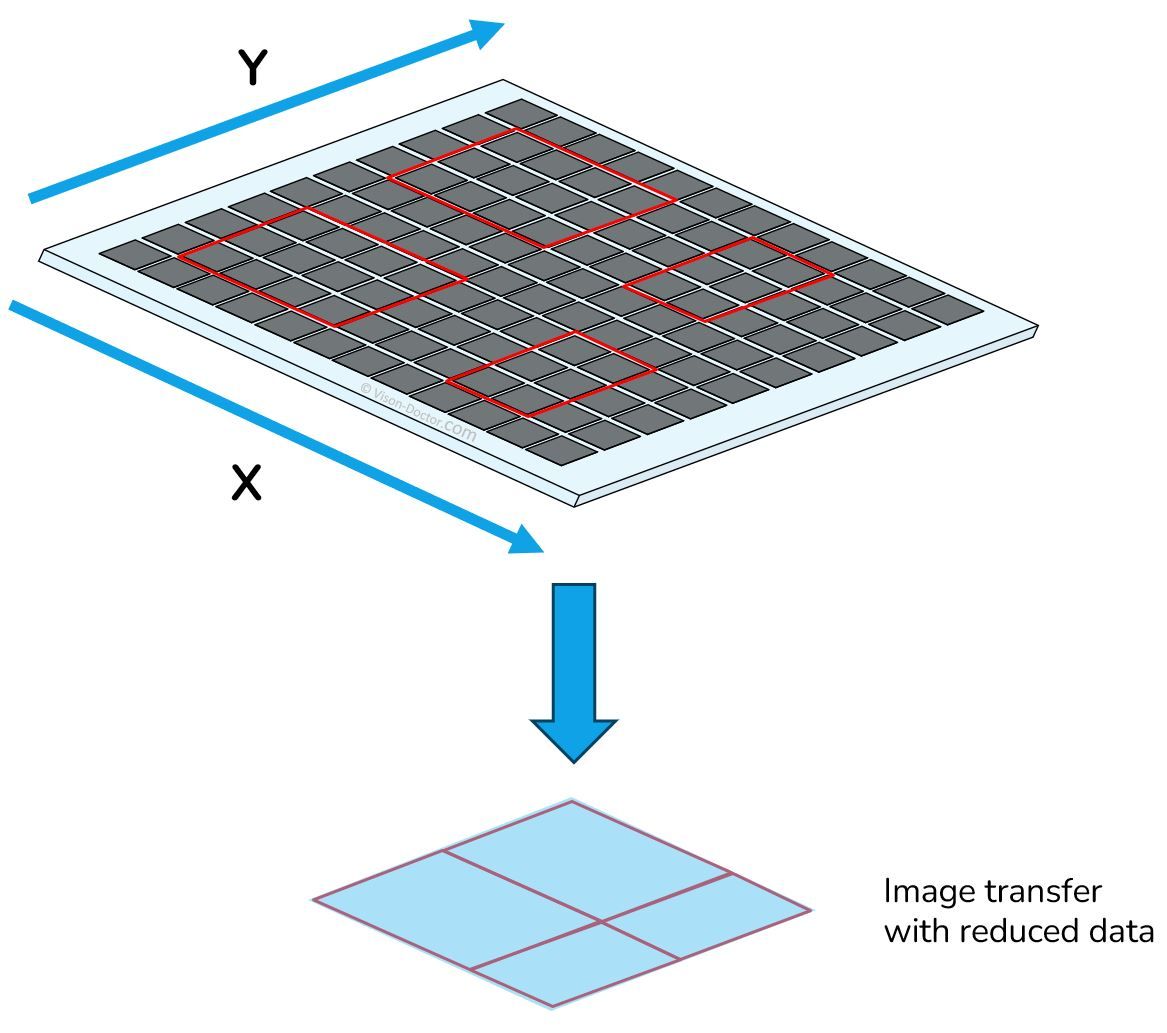
The multi-ROI (Region of Interest) readout function is an advanced technology for industrial cameras that allows several specific areas within an image to be captured and processed simultaneously. This means that not just one image area, but several image areas on the sensor are read out per image capture.
Advantage:
During image capture, only the pixel information within the regions is read from the sensor and transmitted as one image. This means that only the image areas of interest can be condensed into a single compact image, without unnecessary information around the features. The data rate during transmission is minimal.
Vision-Doctor.com is a private, independent, non-commercial homepage project and not a technology provider or system integrator. Suitable technologies and further professional support can be obtained from the companies & partners listed below.
If necessary, I will be happy to provide a quick recommendation, contacts and brief information.
