





















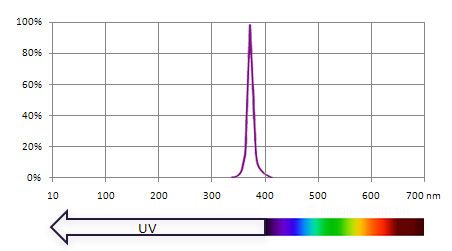
Another option for highlighting features is the use of ultraviolet radiation, which can have a wavelength of 10 to 400 nm. Using fluorescent lamps ('black light') or ultraviolet LEDs, it is quite easy to produce UV radiation with a wavelength of 365 nm in the 'near UV-A' range.
Please check the photobiological safety of UV lighting. As the human eye can no longer detect UV radiation, there is no eyelid closure reflex. UV LEDs are therefore often no longer in LED Risk Class 1, but in LED Risk Class 2, for example. Shielding, enclosure and labelling are mandatory.
However, even in this UV-A range, standard lenses absorb a large proportion of the light that is emitted. This also applies to standard camera system optics, filter glasses and even the protective glass on the sensor. Nevertheless, many applications can be solved with standard components, as excitation with UV radiation causes fluorescence in the visible range in certain materials.
However, real UV applications in shorter wavelength light ranges require special optics, e.g. made of quartz glass, and special camera sensors with suitable detectors.
Normal CMOS sensors are only UV sensitive up to 370nm. Normal CMOS sensors are only UV sensitive up to 370nm. However, there is now a simple solution, as SONY has launched the 'Pregius S IMX 487' sensor with 8 megapixels (2.74µm, 193 fps). Its sensitivity ranges from 200 to around 1000 nm and is in the product portfolio of many camera manufacturers.
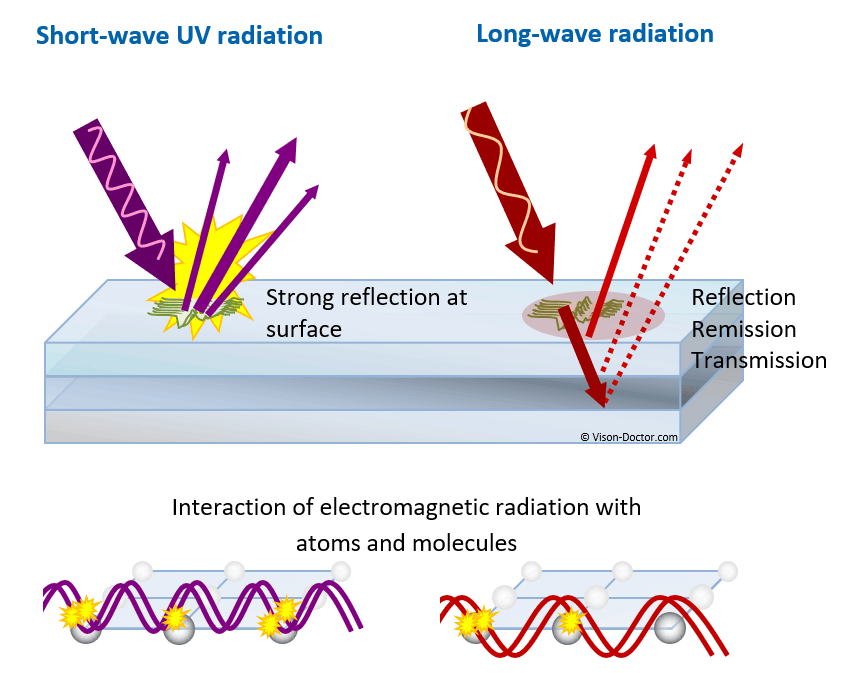
Short-wave radiation tends to be reflected more strongly than long-wave radiation because the short-wave vibrations cause strong interaction even at low penetration depths into the material.
UV radiation is therefore ideal for surface inspection. Small features, dust and scratches are particularly visible.
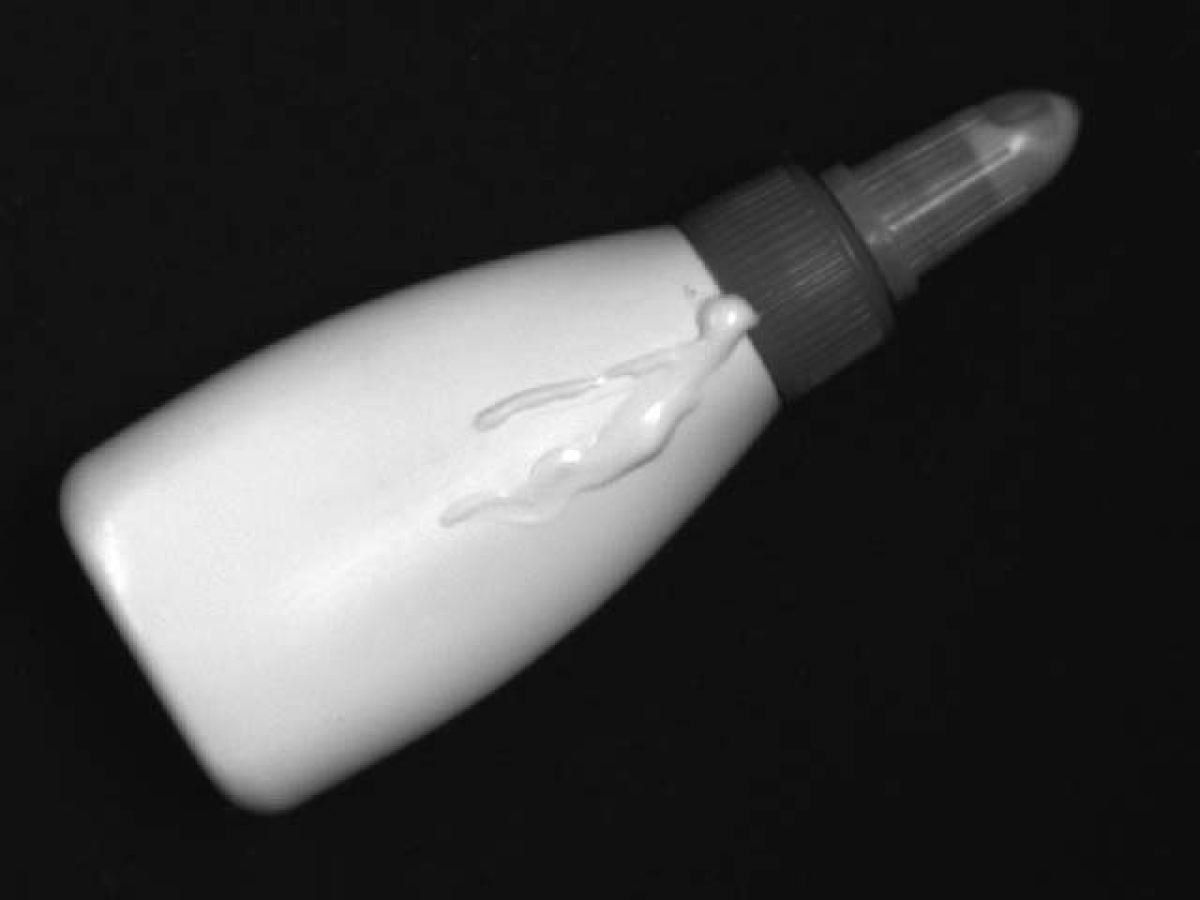
There are also many applications where the material to be inspected is made to glow in the visible by UV radiation.



Vision-Doctor.com is a private, independent, non-commercial homepage project and not a technology provider or system integrator. Suitable technologies and further professional support can be obtained from the companies & partners listed below.
If necessary, I will be happy to provide a quick recommendation, contacts and brief information.
